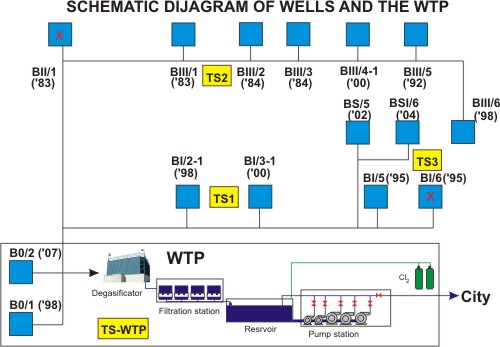
In the past and present time the town of Becej has orientated towards the subterranean water resources when the water supply is concerned. In the earlier stage of the development of this area, the subterranean water of freat springs, that is shallow water bearing layer, was used as a resource. The deep water bearing layer with the scooping of so called “yellow water” was partially used. In the mid-seventies water bearing layers between 60m and 170m were determined by means of hydrogeological researches. Several layers, unevenly distributed, make the basic water bearing complex for the water supply system. Those are mainly lithospheric formations built of small-grain sands, and less often of medium-grain sands. The virility of collector layers range from 8m to 15m. The maximum capacity of researched area is estimated to about 530 l/s. On the basis of well water-interventions realized so far, the total capacity is about 100 l/s currently, and the catchments layers in the depth of between 70m and 130m stand out. According to lithospheric composition, these layers represent small-grain to dust sands with the average quotients of filtration between q=10-4 to 10-5 m/s. Sand collectors are mutually separated by virile clay layers – insulators, even 10 m in depth. It is estimated that collectors still make one unique hydrogeological environment, mutually separated by insulation layers in places.
Since the year 1980 until today 24 individual water interventions have been performed. In the technology of well drilling the methods of reverse and classic drilling have been applied. The wells drilled by the reverse method have the drilling diameter 800-1000mm, the column diameter 323-400mm and the filter diameter 323-400mm. The wells with the classic method of drilling have the drilling diameter 323-440mm, the column diameter 323mm and the filter diameter 219-323mm. The wells are equipped with different filter constructions (Johnson, bridge, Gavrilko, sceleton-wound and similar). The suggested exploitation capacity is about 15 l/s for the wells with the reverse, that is about 10 l/s for the wells with the classic method of drilling. In respect of the decrease of well capacities in the function of time, since the year of 1992, the regeneration of atrophied wells by methods of physical, chemical and hydraulical regeneration has been performed. On the existing wells 13 wells are exploited, with the abundance of 3-16 l/s. The general decrease of piezometric levels on the location of wells decreases 0,5m annually. The chemical composition of the scooped subterranean waters is mainly appropriate, although the content of certain elements exceeds the approved concentrations determined by the Rule book. These elements are brought into limits determined by the Rule book by the system of conditioning. The hardness of water is about 14 German degrees. The total content of gasses in water amounts to 17 l/m3 and it consists of methane, hydrogen-sulfide and carbon dioxide. The content of iron and ammonia is increased in the subterranean waters which is characteristic for the raw water from the used hydrogeological area. The content of arsenic in the raw water does not exceed the limits determined by law. The management and supervision over wells is done from the water factory via PLC (starting, stopping, level, water flow, pump electricity, alarms) Pumps (EMU, Pleuger, Lowara, Franklin) are placed in the depth of 30m, thrusting pipes are 100mm, the management is performed with the older ones via Y/D contactors and with the newer ones via soft starters and frequency regulator. The series of subsequent breakdowns on the 20 kV underground power cables during May and June indicates the fact that they are technically worn-out and their replacement is necessary for 2,700 m in the total length.
Current problems
- lack of water quantities on the market
- presence of floating (dust) sand in water
- relatively fast atrophy (aging) of wells
- lack of construction of the information-management system of well functioning with the older wells
- lack of links of all transformer stations with the underground HV power cables
- lack of measuring instruments for the water flow and measuring of levels with the older wells
- lack of spare well pump
- technically worn-out state of 20 kV of underground cables
Elements of development
- Annual drilling of one well
- physical, chemical and hydraulic revitalization of three wells annually
- preparation of the elaboration on the exploitation of wells
- acquisition of the missing measuring-regulation equipment
- construction of the information-management system of well functioning with the older wells
- equipping of the transformer station
- replacement of 20 kV underground power cables